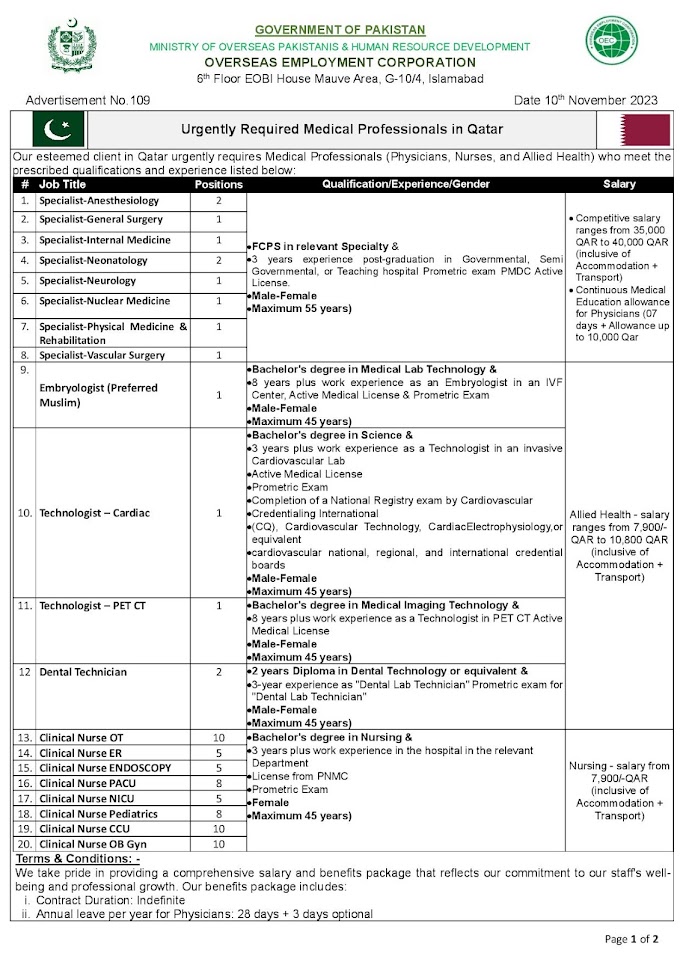
Fasting, or abstaining from food and drink for a certain period of time, has been practiced by various cultures and religions for centuries. In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in the potential health benefits of fasting. In this blog post, we will explore the scientific evidence behind some of the benefits of fasting.
- Weight loss
Fasting can lead to weight loss, as it reduces calorie intake. When the body is in a fasting state, it burns stored fat for energy instead of glucose from food. A study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that intermittent fasting was an effective way to reduce body weight and body fat.
- Improved insulin sensitivity
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. Fasting has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, as the body is forced to use stored glucose for energy during the fast. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that alternate-day fasting improved insulin sensitivity in overweight adults.
- Reduced inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response by the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can contribute to various diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease. Fasting has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. A study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that alternate-day fasting reduced levels of inflammatory markers in overweight adults.
- Improved cardiovascular health
Fasting can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. It has been shown to reduce blood pressure, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol levels (also known as "bad" cholesterol). A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that intermittent fasting improved various markers of cardiovascular health in adults at risk for heart disease.
- Increased longevity
Fasting has been shown to increase lifespan in various animal studies. It is thought that fasting activates various cellular repair mechanisms in the body. A study published in the journal Cell Metabolism found that intermittent fasting increased lifespan in mice.
Fasting has various potential health benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, improved cardiovascular health, and increased longevity. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any fasting regimen, as it may not be appropriate for everyone. Additionally, it is important to ensure that adequate nutrition is consumed during non-fasting periods.
- Improved brain function
Fasting has been shown to improve brain function and protect against age-related cognitive decline. A study published in the Journal of Neuroscience found that intermittent fasting improved cognitive function and increased the growth of new nerve cells in the brain in mice. Another study published in the Journal of Physiology found that intermittent fasting improved memory and learning in mice.
- Reduced risk of cancer
Fasting may help reduce the risk of cancer. A study published in the journal Cancer Cell found that fasting reduced the growth and spread of tumors in mice with various types of cancer. Another study published in the journal Aging found that intermittent fasting reduced the incidence of breast cancer in mice.
- Improved immune system function
Fasting has been shown to improve immune system function. A study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that alternate-day fasting improved immune system function in overweight adults. Another study published in the journal Cell Stem Cell found that fasting increased the production of new immune cells in mice.
- Reduced oxidative stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, which can lead to various diseases. Fasting has been shown to reduce oxidative stress in the body. A study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that alternate-day fasting reduced oxidative stress in overweight adults.
- Improved gut health
Fasting may help improve gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and reducing inflammation in the gut. A study published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe found that intermittent fasting increased the diversity of gut bacteria in mice and improved gut barrier function.
Overall, fasting has numerous potential health benefits supported by scientific research. However, as with any lifestyle change, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that fasting is appropriate for your individual needs and health status.




.jpeg)
.jpg)